Trust when we hear this word the first thought that comes to our mind is that somebody is good, honest, sincere, etc., and will not try to harm or trick you.
And this belief builds a strong foundation and confident society but what happens if you trust some organizations where there is a lot of storytelling and selling dreams which lead you to invest your hard earn money in the organization where you don't know what happens behind the doors?
Unfortunately, this is happening where mismanagement by some large corporations creates a domino effect in the whole economy in the form of inflation
![]()
A few dozen account holders waited outside a San Francisco branch of stricken Silicon Valley Bank -- which was seized by regulators
Expectations and Essence of web 3
Web 3 is an idea for a new iteration of the World Wide Web which incorporates concepts such as decentralization, blockchain technologies, and token-based economics.
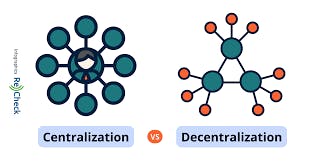
- Decentralization - this basically means they want to transition to a model of the internet where big companies aren't the main providers of online services. E.g. Google provides email, maps, search services, chat apps, etc. Along with the provision of those services most of them free, they profit from monetizing your aggregated data to provide advertising. Web3 proponents imagine a reality where these services aren't controlled by one entity like Google on their servers but distributed along individual nodes instead perhaps computers like you and I are on.
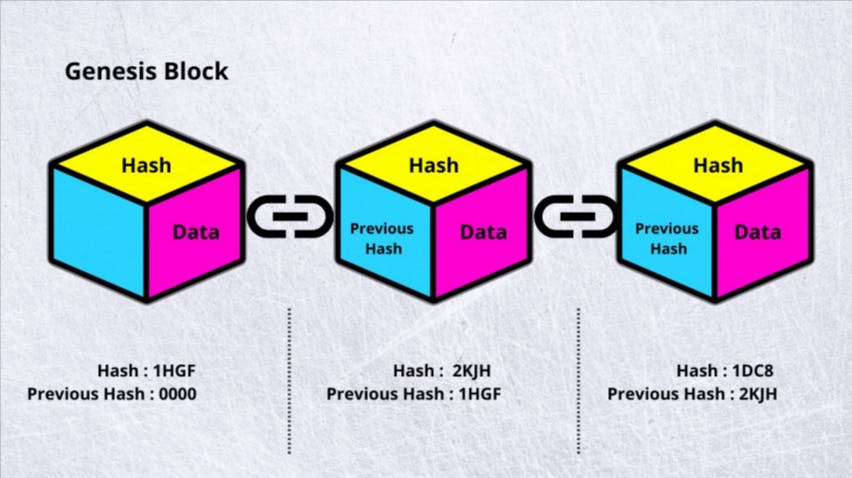
Blockchain - A blockchain is a distributed database or ledger shared among a computer network's nodes. They are best known for their
crucial role in cryptocurrency systems for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions, but they are not limited to cryptocurrency uses. Blockchains can be used to make data in any industry immutable—the term used to describe the inability to be altered.
Token-based economics - the crypto coins produced by the blockchain had no initial value besides being traded as a "currency" so some folks had the idea to use those tokens as currency for NFTs. Why NFTs? Because you could use regular currencies like dollars and euros for pretty much anything else in life. So instead they made something that specifically needed these new crypto coins (tokens) to purchase and sell.
How does Blockchain work
Transaction initiation: A user initiates a transaction by creating a digital record of it and broadcasting it to the network of nodes.
Verification: The network of nodes checks the transaction to ensure that it is valid and not fraudulent. They verify that the sender has the necessary funds and that the transaction meets the network's rules and requirements.
Block creation: Once the transaction is verified, it is added to a block of other transactions. Each block contains a unique code, known as a hash, which identifies the block and all of the transactions contained within it.
Consensus: The nodes on the network use a consensus mechanism to agree on the order of the blocks and the validity of the transactions. This helps to prevent double-spending and ensures that the network is secure.
Block addition: Once a block is verified and agreed upon, it is added to the blockchain. The blockchain is a decentralized ledger that contains a record of all transactions on the network.
Mining: In some blockchain networks, users called miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to create new blocks and earn rewards in the form of cryptocurrency. This process is called mining, and it helps to secure the network and incentivize participation.
Smart contracts: Many blockchain networks support the use of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written into code. Smart contracts can be used to automate certain transactions and enforce the terms of the agreement.
What is Consensus Mechanism?
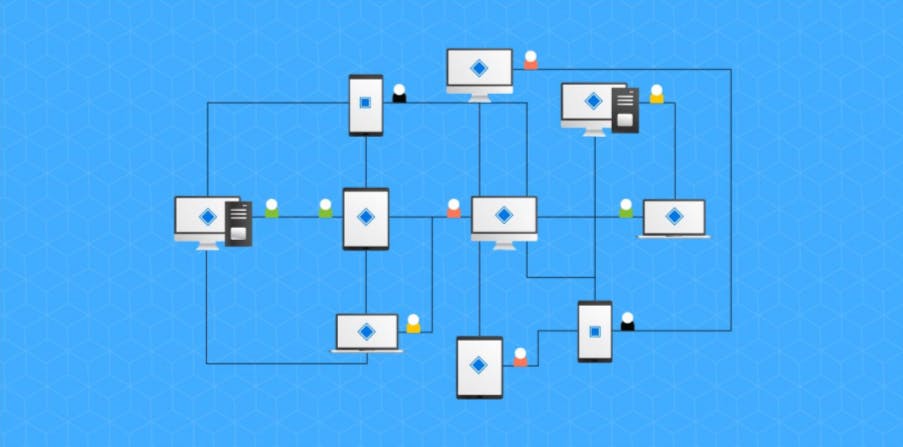
A consensus mechanism is a process used in blockchain technology to ensure that all the nodes or participants in the network agree on the state of the ledger. In other words, it is a way of reaching a distributed consensus without the need for a centralized authority or intermediary.
Consensus mechanisms are necessary for blockchain because there is no central authority or single source of truth to determine the validity of transactions. Instead, multiple nodes on the network have to agree on the validity of each transaction and the order in which they should be added to the blockchain.
There are several types of consensus mechanisms used in blockchain technology, including Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT). Each mechanism has its own set of rules and requirements for achieving consensus.
Proof of Work (PoW):

this is the original consensus mechanism used in Bitcoin and many other blockchain networks. It involves nodes on the network competing to solve complex mathematical problems in order to add a new block to the blockchain.
Proof of Stake (PoS):
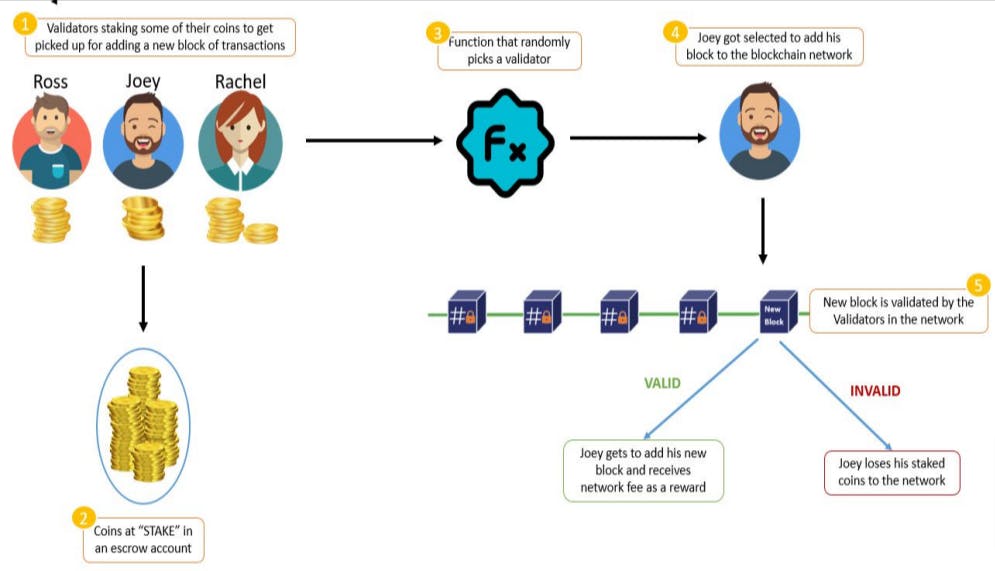
this is a newer consensus mechanism that requires nodes to stake their cryptocurrency holdings in order to participate in the consensus process. The more cryptocurrency a node holds, the more likely they are to be selected to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain.
Pros and Cons of Blockchain
For all of its complexity, blockchain’s potential as a decentralized form of record-keeping is almost without limit. From greater user privacy and heightened security to lower processing fees and fewer errors, blockchain technology may very well see applications beyond those outlined above. But there are also some disadvantages.
Pros
Improved accuracy by removing human involvement in verification
Cost reductions by eliminating third-party verification
Decentralization makes it harder to tamper with
Transactions are secure, private, and efficient
Transparent technology
Provides a banking alternative and a way to secure personal information for citizens of countries with unstable or underdeveloped governments
Cons
Significant technology costs associated with some blockchains
Low transactions per second
History of use in illicit activities, such as on the dark web
Regulation varies by jurisdiction and remains uncertain
Data storage limitations
Summary
Trust is an essential foundation for a healthy society. However, misplaced trust in organizations with shady practices can have severe consequences, such as mismanagement leading to inflation. Enter Web 3, the idea for a new iteration of the World Wide Web that incorporates decentralization, blockchain technologies, and token-based economics. Decentralization aims to transition the Internet away from being controlled by big companies and toward a distributed model. Blockchain is a distributed database that allows for secure and decentralized record-keeping. Token-based economics use cryptocurrency to enable unique transactions.
